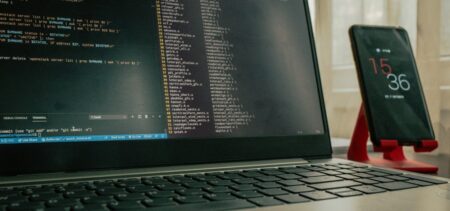
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand into more areas of business, there is an increasing recognition that 5G private networks can now be used more widely for specialized enterprise services and that they can deliver significant ROI through the transformation of private networking infrastructure. The concept of dedicated private mobile networks is not a new one, but with the advent of ultrafast 5G networks, they are starting to attract more interest. Let’s take a look at the most prominent cases and the top benefits of 5G private networks.
What Is a Private 5G Network and How Is It Different from Public 5G?
3GPP, the mobile telecommunications standards organization, refers to private LTE and 5G networks as “non-public networks”. These networks use licensed, shared, or unlicensed wireless spectrum and LTE or 5G cellular networking base stations, small cells, and other Radio Access Network (RAN) infrastructure to transmit voice and data to edge devices, including smartphones, embedded modules, routers, and gateways. Technically, private networks work the same as public LTE and 5G networks. The difference resides in who has a license or priority access to the wireless spectrum, and who owns and operates the network’s base stations and infrastructure.
“With Full Private LTE and 5G networks the organization owns the wireless spectrum it uses for the network, as well as the network base stations and other infrastructure. This provides it with full control over the network and allows it to completely isolate its users from other MNO public networks,” Sierra Wireless explains in a blog post.
Though private 5G networks use the same cellular technology as MNOs for their public 5G networks, you can’t just turn on your smartphone or other device and expect it to connect to a private cellular network. Most often, special SIM cards are used for devices connecting to private 5G networks.
The Benefits of 5G Private Networks
Even though Wi-Fi and 4G are already widely used in industrial applications, they were never designed specifically for business applications and have to be adapted to tailor specific needs. Private and dedicated 5G networks offer a wide range of benefits compared with other options, such as Ethernet or Wi-Fi.
According to GSMA’s guide to private and dedicated 5G networks for manufacturing, production, and supply chains, the main benefits are:
- Strict security, privacy, and data isolation requirements
- Flexibility of device movement and deployment efficiency
- Mobile private and dedicated networks can deliver required coverage and capacity with high quality and reliability through 5G ‘Ultra-Reliable, Low-Latency Communications’
- High bandwidth coverage, predictable error and delay characteristics, and device capacity to ensure efficiency and safety
- The transmission delay and error rate are highly predictable for 5G, allowing reliable software-based compensation to be applied
- Bandwidth can be delivered at scale to suit the needs of the enterprise without necessarily being dependent on the wider rollout plans of the public mobile network operator
- Uplink/ downlink bandwidth ratios can be varied, utilizing the new radio interface and Time Division Duplexing (TDD) technology in 5G
- 5G network slicing allows partitioning of devices and applications. This allows further enhancements to data security and containment especially with the deployment of on-site edge computing
- time-critical applications are enabled through the Time Synchronization Network (TSN) features available in 5G networks which support the integration of legacy Ethernet TSN networks
Top Private 5G Networks Use Cases
Manufacturing
Private 5G networks will play a key role in improving the performance of robotics, autonomous vehicles, and other automation technologies. Factories will be able to easily deploy automated guided vehicles (AGV), manufacturing process monitoring, predictive maintenance, and other IoT applications.
Logistics
Logistics is poised to be another important target. Online retailers and warehouse operators could improve the tracking, monitoring, and sorting of packages and shipments, coupled with inventory system integration.
Airports, train stations, arenas, campuses, and any other large public venue
Private networks will enable airports and airlines to upgrade their digital transformation. Large public venues often need strong coverage, both inside and outside their premises. Private LTE and 5G networks can securely deliver full coverage for IoT devices as well as for thousands of employees and visitors/travelers.
Healthcare
By harvesting the huge amount of generated data and combining it with AI, the potential to improve healthcare is limitless. The high reliability of 5G could make it easier to ensure access to mobile connectivity for critical equipment.
Mining, Oil&Gas, Utilities
Oil&Gas and mining facilities are likely to be early adopters of private 5G networks, simply because many of their facilities are located outside the range of commercial networks. Private networks provide reliable connectivity for increased productivity and safety for offshore platforms, drilling rigs, and employees.